Uncategorized
Erectile Dysfunction: Causes and Treatment
Introduction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence, is a condition affecting a man’s ability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual performance. It is common and affects men of all ages but is more prevalent among older adults.
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
ED can have multiple causes, divided into main categories:
- Psychological Causes
- Stress and Anxiety: Psychological pressures from work or relationships can lead to ED.
- Depression: Depression is a common cause of ED. Antidepressant medications can also exacerbate the condition (Rosen, R. C., et al., 2004).
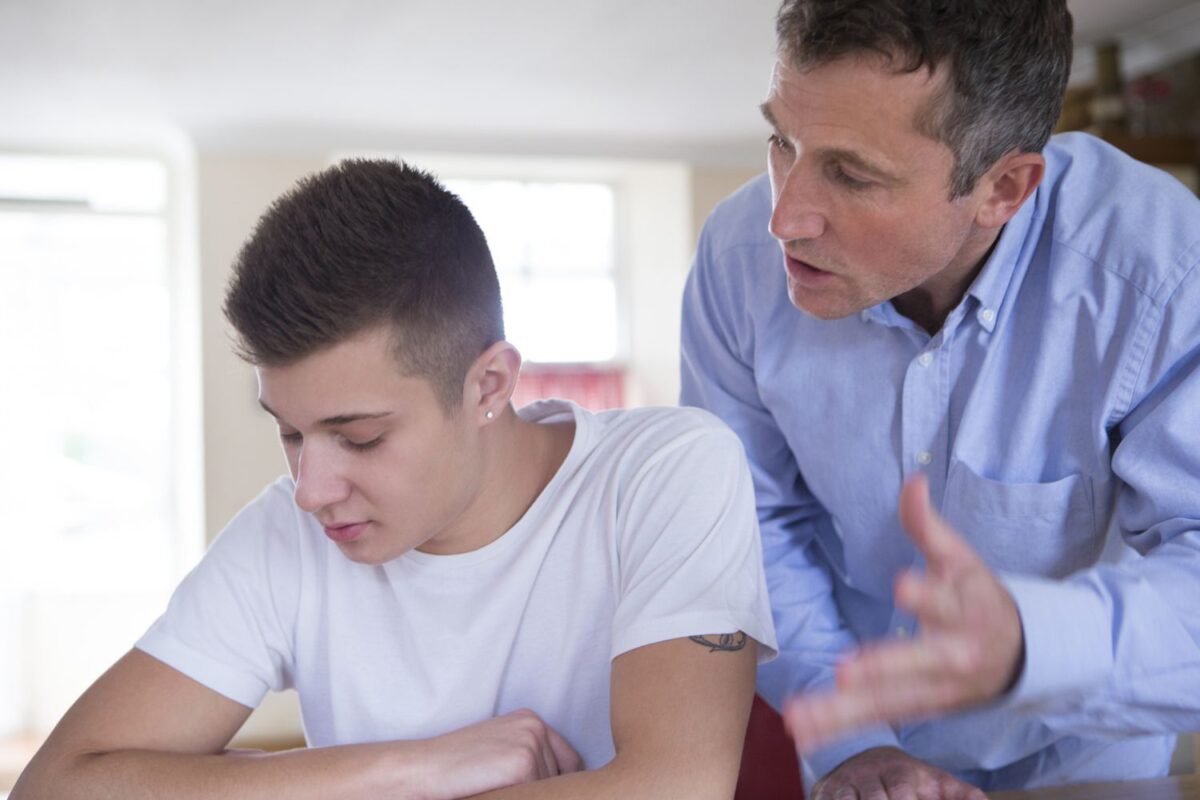
- Relationship Issues: Intimacy problems can impact erectile ability.
- Physical Causes
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease affect blood flow to the penis, causing ED (Kumar, A., et al., 2015).
- Hormones: Low testosterone can affect sexual desire and erection capability.
- Medications: Some drugs, including blood pressure medications, can have ED as a side effect.
- Behavioral Factors
- Smoking: Negatively impacts vascular health, impeding blood flow.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to sexual dysfunction.
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction
- Difficulty achieving an erection.
- Inability to maintain an erection for adequate duration.
- Reduced sexual desire.
- Anxiety or depression related to the condition.
Diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction
Diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical and psychological history, including physical exams and blood tests to check hormone levels and chronic illnesses.
Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
- Psychotherapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Can address anxiety and depression related to ED.
- Couples Counseling: May help improve communication and resolve relationship issues.
- Medication
- PDE5 Inhibitors: Such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) increase blood flow to the penis.
- Hormone Replacement: Used in cases of low testosterone.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves cardiovascular health and enhances sexual performance.
- Quitting Smoking and Reducing Alcohol Intake: Can improve ED symptoms.
- Alternative Treatments
- Herbs and Supplements: Such as ginseng, fenugreek, and maca, but a doctor should be consulted before use.
Conclusion
ED is a common condition that can affect quality of life and personal relationships. It is important to identify underlying causes and seek professional help. Treatment options include psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
References
- Kumar, A., et al. (2015). The management of erectile dysfunction. Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes, 8, 45-54.
- Rosen, R. C., et al. (2004). The relationship between erectile dysfunction and depression. International Journal of Impotence Research, 16(3), 217-224.