Uncategorized
Premature Ejaculation: Causes and Treatment
Introduction
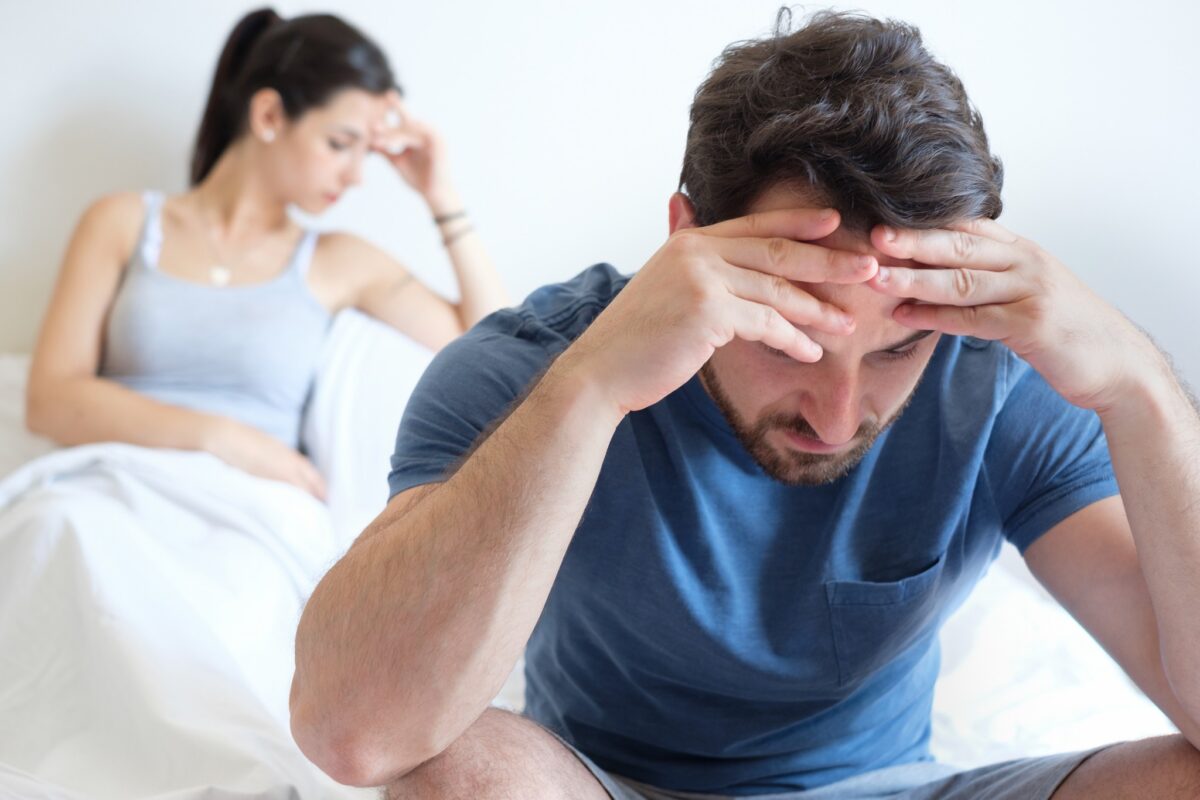
Premature ejaculation (PE) is a common condition affecting many men, where ejaculation occurs before or shortly after penetration. It can cause frustration and anxiety, impacting intimate relationships negatively.
Definition of Premature Ejaculation
PE is characterized by ejaculation occurring sooner than desired, causing a lack of control over timing. It is common among men, especially in youth, but can persist as a chronic issue.
Types of Premature Ejaculation
- Primary PE: Present since the beginning of sexual activity.
- Secondary PE: Develops after a period of normal ejaculatory control.
Causes of Premature Ejaculation
PE can have psychological or physical causes, including:
- Psychological Causes
- Anxiety and Stress: Performance anxiety or life stress can lead to PE.
- Depression: Affects libido and sexual performance, potentially causing PE.
- Past Negative Experiences: Bad sexual experiences can lead to a lack of confidence and increased anxiety.
- Physical Causes
- Health Issues: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease can impact sexual performance and cause PE (Kumar, A., et al., 2016).
- Hormonal Imbalances: Low testosterone can affect sexual drive.
- Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate can influence ejaculation timing.
Symptoms of Premature Ejaculation
- Ejaculation occurring within one minute of penetration.
- Inability to delay ejaculation during sexual activity.
- Frustration or anxiety due to early ejaculation.
Diagnosis of Premature Ejaculation
Diagnosis typically involves evaluating medical and psychological history and discussing symptoms with a doctor. Physical exams may include hormone level analysis.
Treatment Options for Premature Ejaculation
- Psychotherapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps address anxiety and performance-related fears.
- Relaxation Techniques: Meditation and deep breathing can reduce anxiety.
- Medication
- SSRIs: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors like sertraline have proven effective in delaying ejaculation (Khan, M. A., et al., 2014).
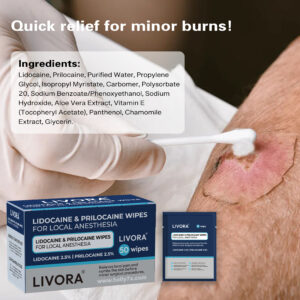
- Topical Anesthetics: Contain local anesthetics like lidocaine to reduce sensation and delay ejaculation.
- Behavioral Techniques
- Squeeze Technique: Involves squeezing the base of the penis to delay ejaculation.
- Stop-Start Technique: Involves stopping sexual stimulation before ejaculation and resuming after some time.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Exercise: Helps improve general health and reduce stress.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports sexual health.
Conclusion
Premature ejaculation is a common condition that can impact quality of life and relationships. It is important to recognize underlying causes and seek specialized help. Treatment options include psychotherapy, medication, and behavioral techniques.
References
- Kumar, A., et al. (2016). The management of premature ejaculation. Clinical Medicine Insights: Urology, 9, 15-24.
- Khan, M. A., et al. (2014). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of premature ejaculation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 11(5), 1174-1185.